JavaScript Proxy
What is a Proxy?
A Proxy is an JavaScript object that can wrap other objects.
A Proxy lets you control operations on other objects.
A Proxy can trap and intercept code when someone is:
- Reading a property (get)
- Setting a property (set)
- Deleting a property (deleteProperty)
- Checking if a property exists (has)
- Calling a function (apply)
- Constructing an object (construct)
Note
A Proxy lets you run your own code when someone interacts with an object.
A Proxy gan be a middleman between your code and a JavaScript object.
Proxy Syntax
const proxy = new Proxy(target, handler);
- target - the original object or function
- handler - an object with trap methods
Example
const myObject = {name: "Jan"};
const proxy = new Proxy(myObject, {
get(target, prop) {
return target[prop];
}
});
Proxy Logging
A typical Proxy example is logging of object changes.
Below is a demo that:
- Wraps an object in a Proxy
- Logs whenever a property is read or written
- Logs each get and set operation in real time
Example
Log all changes to all property values:
// Create an Object
const user = { name: "Jan", age: 40 };
//Create a Proxy
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, property) {
log("Getting: " + property);
return target[property];
},
set(target, property, value) {
log("Setting: " + property);
return target[property];
}
});
proxy.name = "John";
proxy.age = 42;
let text1 = proxy.name;
let text2 = proxy.age
Try it Yourself »
Proxy with Reflect (Most Common)
Below is a demo that:
- Wraps an object in a Proxy
- Logs whenever a property is read or written
- Uses Reflect.get() and Reflect.set() inside the Proxy handlers
- get trap uses Reflect.get(target, property, receiver)
- set trap uses Reflect.set(target, property, value, receiver)
- Reflect makes the Proxy behavior match the normal object behavior
Example
Log all changes to all property values:
// Create an Object
const user = { name: "Jan", age: 40 };
// Create a Proxy
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, property) {
log("Getting: " + property);
// safe forwarding
return Reflect.get(target, property);
},
set(target, property, value) {
log("Setting: " + property);
// safe forwarding
return Reflect.set(target, property, value);
}
});
proxy.name = "John";
proxy.age = 42;
let text1 = proxy.name;
let text2 = proxy.age
Try it Yourself »
Proxy with Reflect Flow
The flow below is the essence of JavaScript metaprogramming with Proxy + Reflect.
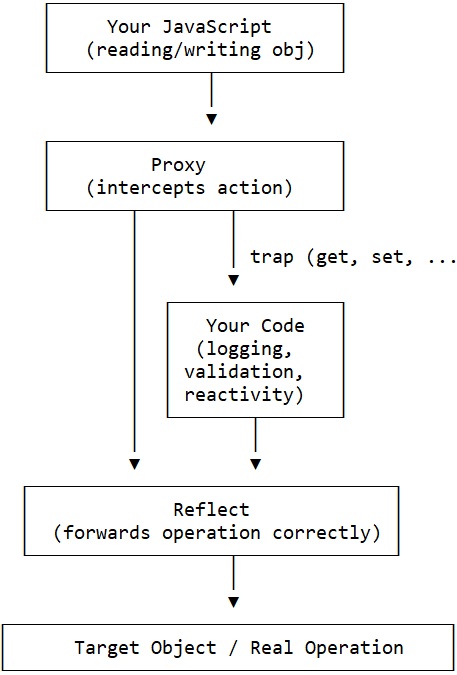
Flow Explanation:
- Your code interacts with an object
- Proxy intercepts the operation
- Your trap code decides what to do
- Reflect forwards the operation safely
- The target object receives the real action
Why Proxies?
Proxies allow you to:
- Add logging
- Validate changes
- Auto-generate properties
- Protect sensitive data
- Create virtual or computed objects
- Intercept function calls
- Create reactive systems (like Vue.js)
Proxy Validation
Example
// Create an Object
const user = { name: "Jan", age: 40 };
// Create a Proxy
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
set(target, prop, value) {
if (prop === "age" && value < 0) {
text = "Age cannot be negative!";
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = text;
}
return Reflect.set(target, prop, value);
}
});
proxy.age = 45; // OK
proxy.age = -5; // Error
Try it Yourself »
Virtual Properties
Example
// Create an Object
const person = {
first: "John",
last: "Doe"
};
// Create a Proxy
const virtual = new Proxy(person, {
get(target, prop) {
if (prop === "fullName") {
return target.first + " " + target.last;
}
return Reflect.get(target, prop);
}
});
let text = virtual.fullName; // "John Doe"
Try it Yourself »
Dynamic Functions
Metaprogramming
Metaprogramming lets JavaScript:
- Intercept behavior
- Modify behavior
- Define new behavior
- Generate behavior dynamically
It gives developers deep control over the language's inner workings.
Proxy Traps
A trap is a function inside a Proxy handler.
It runs whenever a specific operation is performed on the Proxy.
Below is a complete and accurate explanation of every JavaScript Proxy trap, what triggers them, their parameters, and what they are expected to return.
| Trap Name | Triggered when |
|---|---|
| get | A property is read |
| set | A property is changed |
| has | Using the in operator |
| deleteProperty | A property is deleted |
| apply | A function is called |
| construct | An object is cretated (with new) |
| getOwnPropertyDescriptor | A property descriptor is retrieved |
| defineProperty | A property is defined |
| getPrototypeOf | A prototype is retrieved |
| setPrototypeOf | A prototype is set |
| isExtensible | Extensibility is checked |
| preventExtensions | Existenibility is prevented |
| ownKeys | Properties are listed |
Note
The list above is 2025-accurate and includes all 13 Proxy traps defined in ECMAScript.
Each trap handler is decribed below.
handler.get()
Triggered when a property is read:
get(obj, prop, receiver) {
return Reflect.get(obj, prop, receiver);
}
Triggered by:
proxy.property
proxy["property"]
object.property()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property being accessed
- receiver - the this value for getters (usually the proxy itself)
Must Return
- The property value
handler.set()
Triggered when a property is changed:
set(obj, prop, value, receiver) {
return Reflect.set(obj, prop, value, receiver);
}
Triggered by:
proxy.property = value
proxy["property"] = value
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property being accessed
- value - the new property value
- receiver - the this value for setters (usually the proxy itself)
Must Return
- true - if assignment succeeded
- false - to indicate failure
(Throwing is also allowed.)
handler.has()
Intercepts the in operator.
has(obj, prop) {
return Reflect.has(obj, prop);
}
Triggered by:
"property" in proxy
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property being accessed
- receiver - the value of this for setters (usually the proxy itself)
Must Return
- true
- false
handler.deleteProperty()
Intercepts the delete operator.
deleteProperty(obj, prop) {
return Reflect.deleteProperty(obj, prop);
}
Triggered by:
delete proxy.property
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property to delete
Must Return
- true - for sucess
- false - for failure
handler.apply()
Triggered when a function is called:
apply(func, thisArg, args) {
return Reflect.apply(func, this, args);
}
Triggered by:
proxy()
proxy.call()
proxy.apply()
Parameters
- func - the callable object (function)
- this - the this argument for the call
- args - the function arguments array
Must Return
- The return value of the function
handler.construct
Intercepts the new operator.
construct(obj, args, newTarget) {
return Reflect.construct(obj, args, newTarget);
}
Triggered by:
nex proxy()
Parameters
- obj - the constructor object
- args - the array of arguments passed
- newTarget - the constructor
Must Return
- An Object (The new instance)
The construct trap only runs when you use new.
const obj = {} // No trap
Object.create() // No trap
class User {};
new User(); // No trap
handler.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()
Intercepts property descriptor retrieval.
getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, prop) {
return Reflect.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, prop);
}
Triggered by:
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, prop)
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property to describe
Must Return
- A property descriptor
- undefined
handler.defineProperty()
Intercepts Object.defineProperty().
defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor) {
return Reflect.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor);
}
Triggered by:
Object.defineProperty()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prop - the property to describe
- descriptor - the property descriptor
Must Return
- true - if sucess
- false - if not
handler.getPrototypeOf()
Intercepts prototype lookup.
getPrototypeOf(obj) {
return Reflect.getPrototypeOf(obj);
}
Triggered by:
Object.getPrototypeOf()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
Must Return
- An Object
- null
handler.setPrototypeOf()
Intercepts setting the prototype.
setPrototypeOf(obj, prototype) {
return Reflect.setPrototypeOf(obj, prototype);
}
Triggered by:
Object.settPrototypeOf()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
- prototype - the new prototype or null
Must Return
- An Object
- null
handler.isExtensible()
Intercepts checking if an object is extensible.
isExtensible(obj) {
return Reflect.isExtensible(obj);
}
Triggered by:
Object.isExtensible()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
Must Return
- true - for yes
- false - for no
handler.preventExtentions()
Intercepts making an object non-extensible.
preventExtensions(obj) {
return Reflect.preventExtensions(obj);
}
Triggered by:
Object.preventExtensions()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
Must Return
- true - for success
- false - for failure
handler.ownKeys()
Intercepts operations listing keys (property names or symbols).
ownKeys(obj) {
return Reflect.ownKeys(obj);
}
Triggered by:
Object.keys()
Object.getOwnPropertyNames()
Object.getOwnPropertySymbols()
Parameters
- obj - the target object
Must Return
- array of keys with no duplicates
Proxy Traps Map Reflect Methods
A Proxy trap represents one of JavaScript's internal operations:
- [[Construct]]
- [[Call]]
- [[Get]]
- [[Set]]
- [[HasProperty]]
- [[Delete]]
- [[DefineProperty]]
- [[GetOwnProperty]]
- [[OwnPropertyKeys]]
- [[GetPrototypeOf]]
- [[SetPrototypeOf]]
- [[PreventExtensions]]
- [[IsExtensible]]
These internal operations are what JavaScript uses (inside the engine) when you access or modify objects.
When a Proxy intercepts one of these operations, they should be forwarded correctly:
get(target, property, receiver) {
return Reflect.get(target, property, receiver);
}
Reflect is used because Reflect methods are 1-to-1 mirrors of the internal operations.
- They produce correct return values (true/false/descriptor)
- They avoid throwing errors that would break Proxy rules
- They make the Proxy behave like normal JavaScript objects (unless modified)
Note
This is why every Proxy trap has a Reflect method with the same name and signature.
JavaScript Internals Became Reflect
Before ES6 (2015), many fundamental operations did not exist as functions:
| Operation | Before E6 | Problem |
|---|---|---|
| get property | obj[prop] | Not callable as a function |
| set property | obj[prop] = value | Not callable as a function |
| delete property | delete obj[prop] | Operator, not a function |
| check property | "prop" in obj | Operator, not a function |
| construct (new) | new Foo() | Not callable generically |
| get prototypes | Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) | Throws on non-objects |
| define property | Object.defineProperty() | Returns object instead of boolean |
| own keys | Object.keys() | Not complete (misses symbols) |
These were incomplete and inconsistent for Proxy forwarding.
So ES6 (2015) added Reflect:
| Internal Operation | Reflect Method |
|---|---|
| [[Construct]] | Reflect.construct() |
| [[Call]] | Reflect.apply() |
| [[Get]] | Reflect.get() |
| [[Set]] | Reflect.set() |
| [[HasProperty]] | Reflect.has() |
| [[Delete]] | Reflect.deleteProperty() |
| [[DefineProperty]] | Reflect.defineProperty() |
| [[GetOwnProperty]] | Reflect.getOwnProperty() |
| [[OwnPropertyKeys]] | Reflect.ownPropertyKeys() |
| [[IsExstensible]] | Reflect.isExtensible() |
| [[PreventExstensions]] | Reflect.preventExtensions() |
| [[GetPrototypeOf]] | Reflect.getPrototypeOf() |
| [[SetPrototypeOf]] | Reflect.setPrototypeOf() |

