ECMAScript 2025
New Features in JavaScript 2025
The 16th edition of the ECMAScript standard, released in June 2025, includes several enhancements to make JavaScript more readable and efficient.
New Set Features in ES2025
JavaScript 2025 includes built-in methods for set operations, such as intersection(), union(), and difference(), eliminating the need for manual loops or third-party libraries.
| Feature | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| union() | Returns the union of two sets | |
| intersection() | Returns the intersection of two sets | |
| difference() | Returns the difference between two sets | |
| symmetricDifference() | Returns the symmetric difference between to sets | |
| isSubsetOf() | Returns true if this set is a subset of a given set | |
| isSupersetOf() | Returns true if this set is a superset of a given set | |
| isDisjointFrom() | Returns true if this set has no elements in in a given set |
New Iterator Helpers in ES2025
The introduction of an Iterator object provides a functional interface with lazy evaluation, allowing developers to wrap various iterators like Arrays.
A new set of functional operators for iterators (like .map(), .filter(), and .take()) allows for lazy evaluation, improving performance when handling large data streams.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| drop() | Returns an iterator that skips a specified number of elements before yielding the rest |
| every() | Returns true if all elements satisfy a test function |
| filter() | Returns an iterator containing elements that satisfy a filter function |
| find() | Returns the first element that satisfies a test function |
| flatMap() | Returns an iterator by mapping each element and then flattening the results |
| forEach() | Executes a function once for each element in the iterator. |
| from() | creates an iterator object from an iterable |
| map() | Returns an iterator with all elements transformed by a map function |
| reduce() | Applies a reducer function against each element to reduce it to a single value |
| some() | Returns true if at least one element satisfy a test function |
| take() | Returns an iterator that yields a specified number of elements |
Other New Features in ES2025
| Feature | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| RegExp /v flag | An "upgrade" to the /u (unicode) flag | |
| RegExp.escape() | Returns a string where regex characters are escaped | |
| Float16Array | A Typed Array that stores 16-bit floating-point numbers | |
| Math.f16round() | Returns the nearest 16-bit floating point number | |
| Promise.try() | Starts a promise chain for handling promise rejections | |
| Import Attributes | Import attributes allowed in import statements |
Warning
These features are relatively new.
Older browsers may need an alternative code (Polyfill).
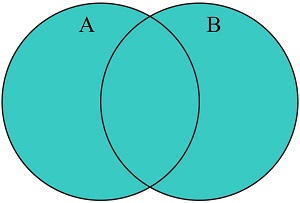
JavaScript Set union()
The union() method returns the union of two sets.
The union() method returns a new set containing the elements which are in this set,
or in the argument set, or in both:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
const C = A.union(B);
Try it Yourself »
The union() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
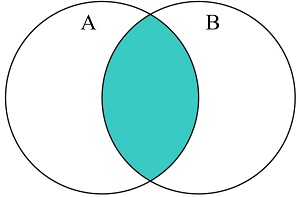
JavaScript Set intersection()
The intersection() method returns the intersection of two sets.
The intersection() method returns a new set containing the elements which are in this set
and in the argument set:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
const C = A.intersection(B);
Try it Yourself »
The intersection() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
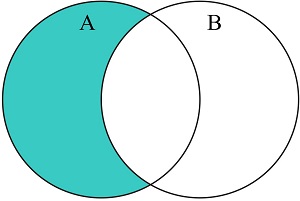
JavaScript Set difference()
The difference() method returns the difference between two sets.
The difference() method returns a new set containing elements which are in this set
but not in the argument set:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
const C = A.difference(B);
Try it Yourself »
The difference() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
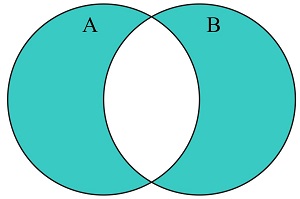
JavaScript Set symmetricDifference()
The symmetricDifference() method returns the symmetric difference between to sets.
The symmetricDifference() method returns a new set containing elements which are in this set
or in the argument set, but not in both:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
const C = A.symmetricDifference(B);
Try it Yourself »
The symmetricDifference() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
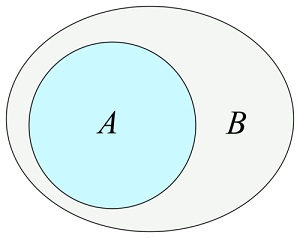
JavaScript Set isSubsetOf()
The isSubsetOf() method returns true
if all elements in this set are elements in the argument set:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
let answer = A.isSubsetOf(B);
Try it Yourself »
The isSubsetOf() method is supported in all modern browsers
since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
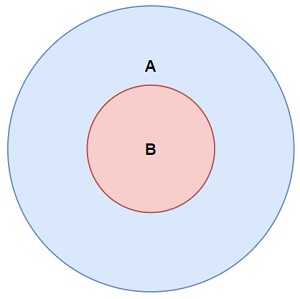
JavaScript Set isSupersetOf()
The isSupersetOf() method returns true if all elements in the argument set are also in this set:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
let answer = A.isSupersetOf(B);
Try it Yourself »
The isSupersetOf() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
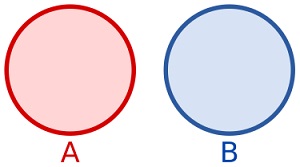
JavaScript Set isDisjointFrom()
The isDisjointFrom() method returns true
if this set has no elements in common with the argument set:
Example
const A = new Set(['a','b','c']);
const B = new Set(['b','c','d']);
let answer = A.isDisjointFrom(B);
Try it Yourself »
The Set.isDisjointFrom() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 122 |
Edge 122 |
Firefox 127 |
Safari 17 |
Opera 108 |
| Feb 2024 | Feb 2024 | Jun 2024 | Sep 2023 | Mar 2024 |
The Iterator.from() Method
The Iterator.from()
creates an iterator object from an existing iterable or iterator object.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([1, 2, 3]);
// Iterate over the elements
let text = "";
for (const x of myIterator) {
text += x;
}
Try it Yourself »
The drop() Method
The drop() method
returns a new iterator that skips a specified number of elements before yielding the rest.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);
// Remove the first five
const firstFive = myIterator.drop(5);
Try it Yourself »
The every() Method
The every(fn) method
returns true if all elements in the iterator satisfy the provided test function.
Example
// Create an Iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from("123456789");
// Is every Element greater than 7?
let result = myIterator.every(x => x > 7);
Try it Yourself »
The filter() Method
The filter() method
returns a new iterator containing elements that satisfy a filter function.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([32, 33, 16, 40]);
// Filter the iterator
const filteredIterator = myIterator.filter(x => x > 18);
Try it Yourself »
The find() Method
The find(fn) method
returns the first element that satisfies a test function.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([3, 10, 18, 30, 20]);
// Find first greater than 18
let result = myIterator.find(x => x > 18);
Try it Yourself »
The flatMap() Method
The flatMap() method
returns a new iterator by mapping each element and then flattening
the results into a single iterator.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);
// Map the Iterator
const mappedIterator = myIterator.flatMap(x => [x, x * 10]);
Try it Yourself »
The forEach() Method
The forEach() method
executes a provided function once for each element in the iterator.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from("123456789");
// Iterate over all elements
let text = "";
myIterator.forEach (x => text += x);
Try it Yourself »
The map() Method
The map() method
returns a new iterator with all elements transformed by a map function.
Example
// Create an iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from("123456789");
// Now you can use the map method
const mappedIterator = myIterator.map(x => x * 2);
Try it Yourself »
The reduce() Method
The reduce() method
applies a reducer function against an accumulator and each element to reduce it to a single value.
Example
// Create an Iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from([175, 50, 25]);
// Reduce the Iterator
let result = myIterator.reduce(myFunc);
Try it Yourself »
The some() Method
The some() method
returns true if at least one element in the iterator satisfies the provided test function.
Example
// Create an Iterator
const myIterator = Iterator.from("123456789");
// Is some Element greater than 7?
let result = myIterator.some(x => x > 7);
Try it Yourself »
The take() Method
The take() method
returns a new iterator that yields at most a specified number of elements.
Example
const myIterator = Iterator.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);
// Take the first five elements
const firstFive = myIterator.take(5);
Try it Yourself »
The RegExp /v Flag
The v flag is an "upgrade" to the u flag.
The u (unicode) flag enables full Unicode support in regular expressions.
The v flag enables more Unicode-related features.
The new features are:
- The \p escape sequence matches strings, instead of just characters.
- The character class is upgraded to allow intersection, union, and subtraction syntaxes, as well as matching multiple Unicode characters.
Examples
let text = "Hello 😄";
let pattern = /\p{RGI_Emoji}/v;
let result = pattern.test(text);
Try it Yourself »
let text = "Hello 😄";
let pattern = /\p{RGI_Emoji}/;
let result = pattern.test(text);
Try it Yourself »
Note
Using both flags (u and v) results in a SyntaxError.
/regexp/v is supported all in modern browsers since May 2025:
| Chrome 136 |
Edge 136 |
Firefox 134 |
Safari 18.2 |
Opera 121 |
| Apr 2025 | May 2025 | Jan 2025 | Des 2024 | Jun 2025 |
The RegExp.escape() Method
The RegExp.escape() method returns a string where characters that belongs
to the regular expression syntax are escaped.
This makes it possible to treat characters like +, *, ?, ^, $, (, ), [, ], {, }, |, and \ literally, and not as part of a regular expression.
Example
Create a regular expression that matches the string "[*]":
// Escape a text for to use as a regular expression
const safe = RegExp.escape("[*]");
// Build a new reglar expression
const regex = new RegExp(safe);
// Text to replace within
const oldText = "[*] is a web school.";
// Perform the replace
const newText = oldText.match(regex, "W3Schools");
Try it Yourself »
RegExp.escape() is supported all in modern browsers since May 2025:
| Chrome 136 |
Edge 136 |
Firefox 134 |
Safari 18.2 |
Opera 121 |
| Apr 2025 | May 2025 | Jan 2025 | Des 2024 | Jun 2025 |
The Float16Array Method
A Float16Array is a TypedArray that stores 16-bit (half-precision)
floating-point numbers in the IEEE 754 half-precision format.
Float16Array requires half the memory of Float32Array
and a quarter of Float64Array.
Example
const myArr = new Float16Array([1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5]);
let bytes = myArr.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
let length = myArr.length;
Try it Yourself »
The Float16Array object is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 135 |
Edge 135 |
Firefox 129 |
Safari 18.2 |
Opera 120 |
| Apr 2025 | Apr 2025 | Aug 2024 | Des 2024 | May 2025 |
The Math.f16round Method
The static Math.f16round() method returns the nearest 16-bit floating point representation of a number.
Example
let a = Math.f16round(2.60);
let b = Math.f16round(2.50);
let c = Math.f16round(2.49);
let d = Math.f16round(-2.60);
let e = Math.f16round(-2.50);
let f = Math.f16round(-2.49);
Try it Yourself »
The Math.f16round() method is supported in all modern browsers since June 2024:
| Chrome 135 |
Edge 135 |
Firefox 129 |
Safari 18.2 |
Opera 120 |
| Apr 2025 | Apr 2025 | Aug 2024 | Des 2024 | May 2025 |
The Promise.try() Method
The Promise.try() method starts a promise chain from potentially throwing, synchronous code.
This ensures exceptions are correctly handled as promise rejections.
Example
function compute() {
return Promise.try(() => {
const v = mayThrowSync();
return asyncFunc(v);
});
}
Modules with Import Attributes
Syntax
import {names} from "module-name" with {key:"data"};
Examples
import config from "config.json" with {type:"json"};
import styles from "styles.css" with {type:"css"};
import data from "data.json" with {type:"json"};

