Tensors
A Tensor is a N-dimensional Matrix:
- A Scalar is a 0-dimensional tensor
- A Vector is a 1-dimensional tensor
- A Matrix is a 2-dimensional tensor
A Tensor is a generalization of Vectors and Matrices to higher dimensions.
| Scalar | Vector(s) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Matrix | Tensor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Tensor Ranks
The number of directions a tensor can have in a N-dimensional space, is called the Rank of the tensor.
The rank is denoted R.
A Scalar is a single number.
- It has 0 Axes
- It has a Rank of 0
- It is a 0-dimensional Tensor
A Vector is an array of numbers.
- It has 1 Axis
- It has a Rank of 1
- It is a 1-dimensional Tensor
A Matrix is a 2-dimensional array.
- It has 2 Axis
- It has a Rank of 2
- It is a 2-dimensional Tensor
Real Tensors
Technically, all of the above are tensors, but when we speak of tensors, we generally speak of matrices with a dimension larger than 2 (R > 2).
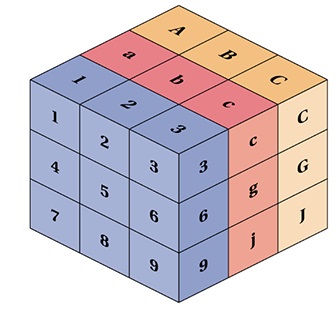
Linear Algebra in JavaScript
In linear algebra, the most simple math object is the Scalar:
const scalar = 1;
Another simple math object is the Array:
const array = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
Matrices are 2-dimensional Arrays:
const matrix = [ [1,2],[3,4],[5,6] ];
Vectors can be written as Matrices with only one column:
const vector = [ [1],[2],[3] ];
Vectors can also be written as Arrays:
const vector = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
Tensors are N-dimensional Arrays:
const tensor = [ [1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9] ];
JavaScript Tensor Operations
Programming tensor operations in JavaScript, can easily become a spaghetti of loops.
Using a JavaScript library will save you a lot of headache.
One of the most common libraries to use for tensor operations is called tensorflow.js.
Tensor Addition
const tensorA = tf.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]);
const tensorB = tf.tensor([[1,-1], [2,-2], [3,-3]]);
// Tensor Addition
const tensorAdd = tensorA.add(tensorB);
// Result [ [2, 1], [5, 2], [8, 3] ]
Tensor Subtraction
const tensorA = tf.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]);
const tensorB = tf.tensor([[1,-1], [2,-2], [3,-3]]);
// Tensor Subtraction
const tensorSub = tensorA.sub(tensorB);
// Result [ [0, 3], [1, 6], [2, 9] ]
Learn more about Tensorflow ...

